Microrobots with autonomous mobility show great promise for targeted drug delivery, driving significant research into their locomotion mechanisms. However, achieving autonomous obstacle avoidance and precise payload release remains a significant challenge. Real-time environmental perception and intelligent path planning are critical for establishing stable closed-loop control systems.
Recently, researchers at the Shenyang Institute of Automation (SIA), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), developed biohybrid diatom microrobots capable of intelligent navigation. By implementing deep learning algorithms for real-time detection of microrobots, obstacles, and targets, the team achieved autonomous path planning, magnetic actuation, trajectory tracking, and targeted delivery.
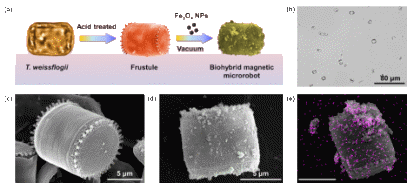
Fabrication of Diatom Microrobots (Image by the research group)
The research team's autonomous control system features three integrated innovations: deep learning detection of microrobots, obstacles, and targets; magnetic actuation guided by adaptive fuzzy PID control for smooth trajectory tracking; and real-time obstacle avoidance through continuous environmental monitoring and path optimization. This closed-loop framework enables fully automated navigation and motion control of the diatom microrobots.
In biological validation experiments using mouse glioma cells as targets and macrophage cells as obstacles, the diatom microrobots demonstrated effective obstacle avoidance and precise target delivery. This generalizable methodology shows significant potential for targeted therapeutic applications.

Movement of Diatom Robots in Different Scenarios (Image by the research group)
The research results were published in IEEE Transactions on Robotics under the title Deep learning-based automatic control of magnetic diatom biohybrid microrobots for targeted delivery. Mengyue Li, a doctoral student at SIA, is the first author, and researchers Niandong Jiao and Lianqing Liu are the corresponding authors.
The SIA team continues to pioneer microrobots for biomedical applications, advancing the integration of microrobotics and medical technologies. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key R&D Program, and CAS Youth Innovation Promotion Association.