Recently, construction methods based on minimum weight distribution (MWD) for polar codes with successive cancellation list (SCL) decoding are proposed by the Industrial Network Group at the Industrial Control Network and System Department of theShenyang Institute of Automation (SIA), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). The relevant research has been published in IEEE Transactions on Communications (TCOM), the top journal of the second region of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in the communications field.
Polar codes have been proved to achieve the capacity of arbitrary binary-input discrete memoryless channels as the code length goes to infinity with the successive cancellation (SC) decoding. However, the performance of polar codes is weak at short to moderate code lengths under SC decoding.
To improve the block error rate (BLER) performance, the researchers proposed a method for the successive cancellation list (SCL) decoding by expanding candidate paths.Since polar codes demonstrate advantages in error performance, complexity and rate matching, they have been adopted as the coding scheme for the control channel of the enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) service category in the fifth generation wireless communication systems (5G). In 5G, polar codes are constructed by a fixed universal polar sequence for all the code configurations by computer searching with the maximum polar sequence length 1024.
Researchers have made breakthroughs in polar code construction across three key dimensions. First, they demonstrated the asymptotic convergence between maximum likelihood performance and the minimum weight union bound (MWUB) as the signal-to-noise ratio approaches infinity. Second, a channel-independent nested construction sequence named the MWD sequence was developed, with rigorous proof establishing its optimality under MWUB evaluation for polar codes satisfying partial order conditions. Building upon the MWD framework, the team further proposed an entropy-constrained bit-swapping (ECBS) construction methodology that systematically swaps information and frozen bits through iterative optimization to satisfy entropy constraints in information set selection, while maintaining structural integrity.
This research provides theoretical foundations and practical solutions for high-performance construction of polar codes in industrial 5G
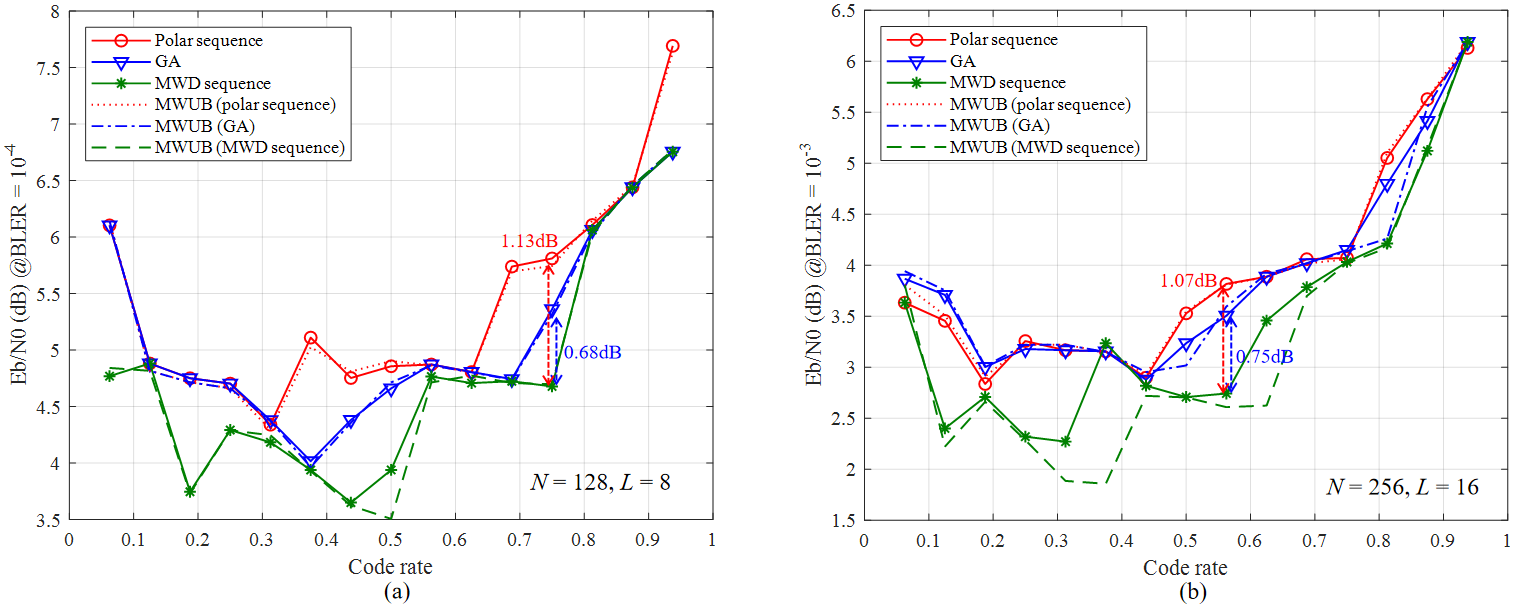
The BLER performance comparison between MWD sequence and polar sequence .(Image by the research group)

The BLER performance comparison between ECBS algorithm and other algorithms (Image by the research group)
The research is supported in part by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, in part by the Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, and in part by the Fundamental Research Project of SIA.
Paper link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10677464
DOI: 10.1109/TCOMM.2024.3458081