In order to tackle the challenges in optimizing design of collaborative robots (cobots), researchers at Shenyang Institute of Automation (SIA), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have recently proposed a multi-objective optimum design method based on orthogonal design experiment(ODE) and finite element substructure method(FESM).
This method takes the natural frequency, the Cartesian stiffness and the mass of the robot as optimization objectives, and can tackle the challenges in optimizing design of collaborative robots, such as the influence of time-varying kinematic configurations and optimization objectives, the calculated amount and the modeling precision of optimization model conflict with each other, and the influence of non-structural parameters on robot performances, etc.
The proposed method can guarantee both the modeling accuracy and the high calculation speed, while taking complex shapes of robot modules into consideration, thus effectively improve the global static and dynamic performance of the cobots. The finding is published onStructural and Multidisciplinary Optimization.
Under the constraints of safety, light weight, and large load-to-weight ratio, it is a challenge for the design of cobots to require higher stiffness and dynamic performances. Structural optimization design provides an effective way to solve this problem. The global elastic deformation index and the global first-order natural frequency index are used to evaluate the global stiffness and dynamic performances of cobots respectively, and then a global multi-objective optimization design method for cobots is proposed.
In the study, the researchers first establish the FESM model of cobots to obtain multiple global performance indexes of robots in real-time and efficiently. The FESM model can preserve the accuracy of the finite element method while ensuring the computational efficiency.
Then, the gray relational analysis method is used to construct the multi-objective optimization function which includes the global first-order natural frequency index, the global elastic deformation index, and the mass of the robot.
The researchers constructed ODE, and according to the orthogonal array, the degree of gray incidence under different levels of influencing factors is solved. This method can reduce the amount of calculation without reducing optimization parameters. And through range analysis, the optimal combination of influencing factor levels can be obtained to guide the structural design of the Cobots.
Based on the above method, they tested the proposed method on SHIR 5, a cobot developed by the institute. And the global performance indexes of SHIR5 robot can be improved effectively after optimization design, which verifies the correctness and effectiveness of this method.
This research is sponsored by the Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Science, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the New Generation Information Infrastructure Construction Project and “Internet plus” Key Project of the National Development and Reform Commission, etc. The researchers systematically researched the optimization design method of mechanism and structure systems of cobots, and achieved a series of high-level research results, which provided theoretical basis and technical support for the design and development of cobots.
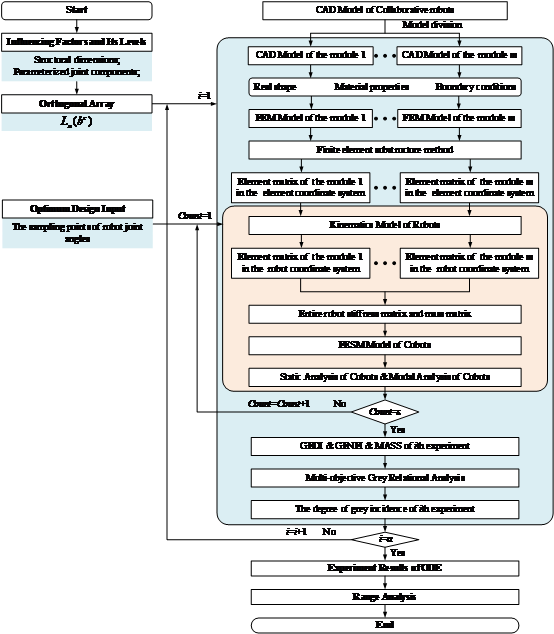
The flowchart of multi-objective optimum design method of Cobots. (Image by SIACAS)
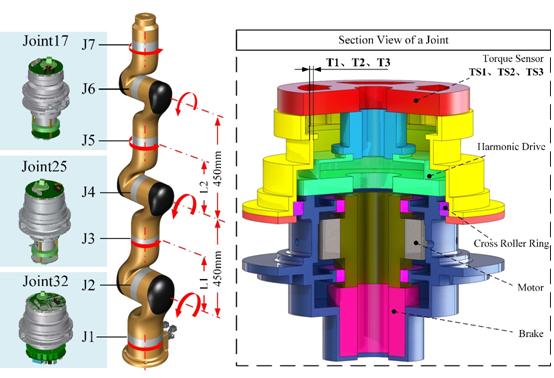
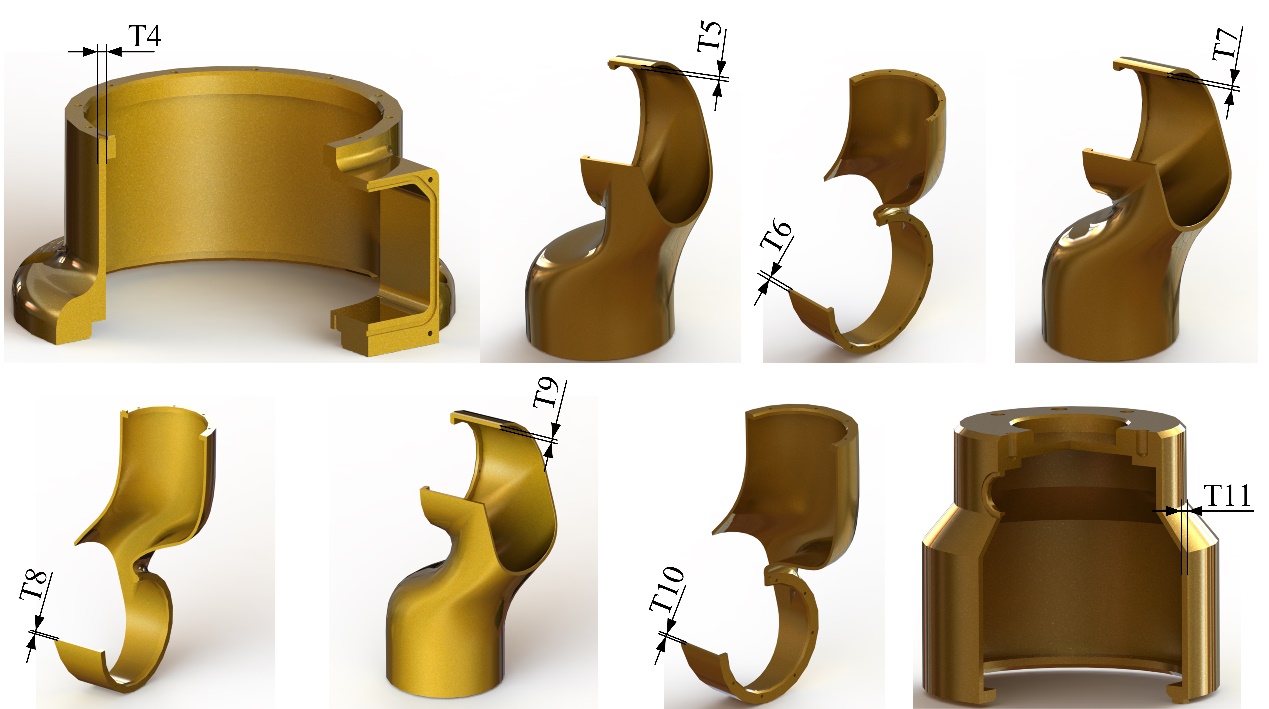
SHIR5 Cobots and the section views of its joint and link modules. (Image by SIACAS)
Contact:
PAN Xin'an
Email: pxa@sia.cn