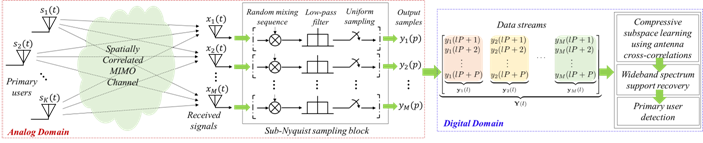
The considered system architecture. (Image provided by SIA)
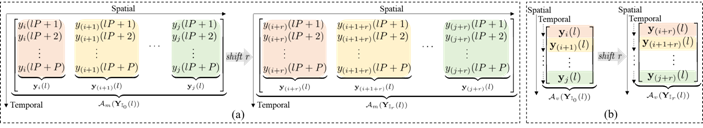
With the continuous enrichment of wireless communication scenarios and the extensive growth of wireless communication equipments and services, the available spectrum resources are increasingly scarce. It is therefore critical to study how to flexibly coordinate and fully utilize the limited spectrum resources of the next-generation intelligent radio.
Wideband spectrum sensing is a primarily important enabling technology for future intelligent radios, which enables wireless devices to have an efficient electromagnetic environment sensing capability, dynamically coordinate each wireless device, and adaptively access unused spectrum resources, thereby increasing the whole throughput and spectrum efficiency.
Recently, the Industrial Communication and System-on-Chip (iComSoC) group at Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has studied the sensing function for the next-generation intelligent radio and proposed high performance wideband spectrum sensing algorithms with the exploitation of antenna cross-correlations and space-time information in multiple-input, multiple-output (MIMO) systems. The study was recently published in IEEE Transactions on Communications.
The research group introduced the information of antenna cross-correlations of multi-antenna systems, and proposed the corresponding compressive subspace learning algorithms. By considering the spatially correlated MIMO channel and depicting the receiving correlation matrix as the exponential correlation model, the analytical relations between the singular values of covariance matrice in the proposed and the traditional algorithms were established.
Next, by deriving the gain (gain upper and lower bounds) over the singular values in the traditional algorithm, the performance superiority of the proposed algorithm was shown. The corresponding theoretical results can further be used to guide the selection of parameters in the proposed algorithms, as well as the design of multi-antenna systems.
Their work provided an effective approach for achieving highly reliable spectrum sensing for next-generation intelligent radios.
In recent years, the iComSoC group has been working on the scientific frontier of sensing and communication for the next-generation wireless communication systems, and putting forward effectively scientific approaches. Several research works have been published by international journals such as IEEE's TCOM, TVT, SJ and so forth. The group will further conduct in-depth research on related fields of the next-generation wireless communications, and make the work hierarchical and structured.
Contact:
DAI Tianjiao
Email: daitianjiao@sia.cn
The considered sub-sample arrangements: (a) matrix form, (b) vector form.(Image provided by SIA)

Performance comparison of WBSS in terms of SNR.(Image provided by SIA)