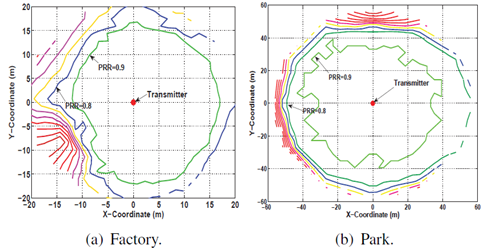
Link reliability test in practical environment. (Photo by Meng ZHENG)
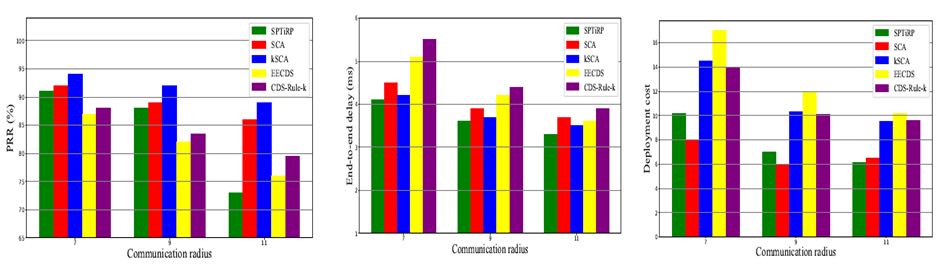
Performance comparison between the proposed method and conventional methods. (Photo by Meng ZHENG)
Since sensor nodes in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are cheap and powered by batteries, their capabilities in communication and energy supply are relatively weak and limited. The deployment of relay nodes in constructing robust network topology can significantly enhance connectivity and reduce energy consumption of WSNs.
However, relay nodes are usually very expensive, thus conventional placement methods only optimize the deployment cost subject to the connectivity constraint. With a mounting of WSNs application in the field of industrial automation and smart grid, timeliness and reliability must be considered.
To solve this problem, the research group on Industrial Wireless Networks at Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIA) proposed a novel relay node placement method for wireless sensor networks (WSNs) which serves as a solid foundation to guarantee the real-time and reliable transmission of WSNs.
The study was published on IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, a top journal in the field of wireless networks and mobile computing, titled Relay Node Placement in Wireless Sensor Networks: from Theory to Practice.
The research team, led by Professor Wei LIANG and Professor Meng ZHENG, proposed for the first time a relay deployment method for WSNs in practical environment.
First, the large-scale relay deployment problems are decomposed into sub-problems by levels, and shortest path tree is employed to eliminate the deployment locations that cannot fulfill the timeliness constraint. In doing so, the deployment in each level is reformulated as an unconstrained set covering problem.
Then, based on extensive experiments in practical environment, the team proposed a relay location adjustment (RLA) algorithm that can adjust relay location according to link reliability measurements.
By combining RLA and a classical set covering algorithm, the proposed method yields obvious performance advantage in terms of timeliness, reliability and deployment cost over conventional methods.
During the past few years, SIA has made significant progress in the research on industrial wireless networks, including network deployment, reliable networking methods, resource allocation, heterogeneous wireless coexistence, analysis and modeling of international standards, and so on. The related results have been published on world renowned journals.
Contact:
Meng ZHENG
Email: zhengmeng_6@sia.cn