Recently, the research group on Industrial Wireless Networks at Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIA) proposed a novel clustering protocol for cognitive radio sensor networks (CRSNs) which can significantly enhance the lifetime and stability of wireless sensor networks. The study was published on IEEE Internet of Things Journal, a top journal in the field of Internet of Things, titled NSAC: A Novel Clustering Protocol in Cognitive Radio Sensor Networks for Internet of Things.
With the proliferation of wireless technologies, wireless sensor networks and other wireless networks, such as WiFi, Bluetooth and so on, are coexisting over the licensed-free ISM 2.4GHz band. Consequently, the coexisting interference will sharply degrade the transmission performance of wireless sensor networks. CRSNs could be a potential solution that combines cognitive radio technology and wireless sensor networks. CRSNs allow sensor nodes to access the licensed bands with high quality dynamically, which significantly increases the transmission performance of wireless sensor networks.
However, the dynamic spectrum leads the frequent variation in the topology of CRSNs and further heavy networking overhead. Cluster-based management methods could effectively reduce the networking overhead, and thus, the design of clustering protocol has become a hot topic in the community of CRSNs.
The research team, led by Professor LIANG Wei and Professor ZHENG Meng, proposed for the first time a network stability aware clustering (NSAC) protocol for CRSNs.
In a network stability-aware clustering (NSAC), each node searches for the maximum edge biclique based on its neighbors and available channels. The weight of each node is calculated based on the remaining energy, the numbers of nodes and available common control channels in its maximum edge biclique.
Then, the node with the largest weight in the neighborhood will be selected as the cluster head, and the rest of nodes in the neighborhood will join the cluster as members. As energy consumption and spectrum dynamics are sufficiently considered in the clustering process, network lifetime and network stability are noticeably enhanced.
Extensive simulations show that the proposed NSAC protocol for CRSNs obviously outperforms existing methods in the aspects of network stablility and energy consumption.
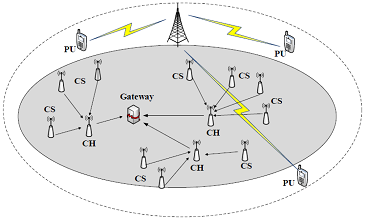
A cluster-based CRSN (Photo by ZHENG Meng)
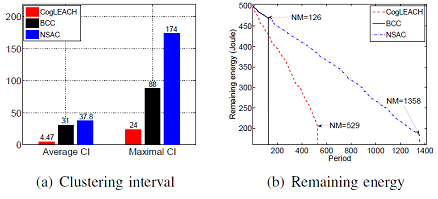
Comparison results between NSAC and existing works (Photo by ZHENG Meng)
Contact:
ZHENG Meng
Email: zhengmeng_6@sia.cn