Infrared small target detection has been widely used in many fields such as surveillance and precision guidance. Because of a long imaging distance, targets usually occupy only a tiny part in the field without a fixed shape. And due to the influence of meteorological conditions such as atmospheric refraction and scattering, the target is too weak to detect. These factors make infrared small targets detection challenging.
Recently, researchers from Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a 3D image-patch tensor (IPT) model to detect infrared small targets. The research results were published in Infrared Physics & Technology.
In order to preserve the correlation between pixels and avoid the image vectorization, researchers constructed an IPT model. The model extended the detection task from the 2D image space to the 3D tensor space.
Researchers found that the size and brightness of small targets always change. But compared with the whole image, small targets occupied only a few parts. Therefore, the foreground IPT T was considered as sparse, and characterized as: ||T||0 <k.
The background image was usually cloud or sea level, and the intensity changed gently, without salient regions. These backgrounds were also slightly blurred due to atmospheric and optical effects in remote imaging. Therefore, the rows and columns of background were regarded as linearly correlated, and the rows and columns of each image patch were also linearly correlated. Each patch was represented by a low-rank matric. When all patches were stacked into a patch tensor, it was represented by a low tubal rank tensor i.e.,rankt(B) < r.
Researchers solved an optimization problem to separate B and T. After reconstruction operation, the foreground image and background image were obtained. Although the foreground image contained a little noise, the noise was removed after a simple filtering. Finally, a small target was easily detected through threshold segmentation.
The study can detect small targets precisely under complex background and keep a high signal-to-clutter ratio (SCR).
This work makes full use of the imaging characteristics of infrared small target images. It provides a new idea for infrared small target detection. Researchers also hope that this work can provide some references in practical application.
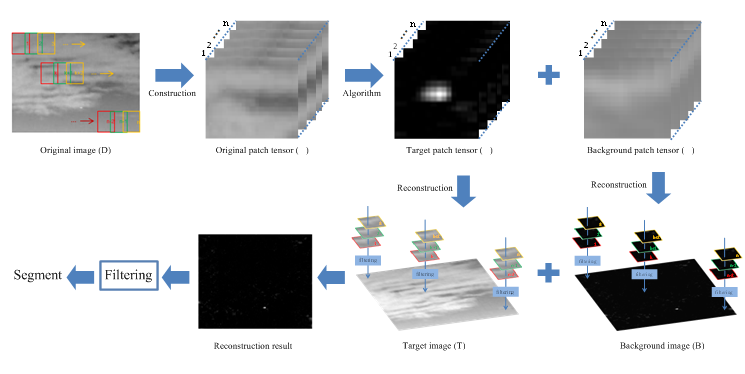
The process of the IPT method. (Image by ZHANG Xiangyue)