A Chinese research team demonstrated a terahertz (THz) imaging deconvolution method which is able to image at the sub-spot level to achieve high-resolution THz images.
This work was done by QI Feng and his team at Terahertz Imaging Laboratory in Shenyang Institute of Automation.
THz imaging is quite promising in scientific and biomedical applications. Current spatial resolution of THz imaging systems is not satisfied due to its much longer wavelength compared to visible light. Many scientists have been working on near-field imaging systems to achieve a high resolution image. However, in this system objects have to be placed extremely close to the sensors, which is not easy for many practical applications.
How to extract information beyond the physical limit of the beam size is important, implying that we will be able to see the object much better by solving the inverse problem. Generally, imaging is considered to be a convolution process and the point spread function essentially blurs the figure. THz light, as a kind of electromagnetic waves, has both amplitude and phase information. Optical image processing algorithms are based on geometrical optics and only intensities are considered.
In this study, published in IEEE Access, phase information of THz waves is fully utilized by making use of the wave nature of THz light. It demonstrated that the reconstructed phase can also describe the shape of the object by applying such an approach.
To evaluate the spatial resolution quantitively, QI and his co-workers fabricate a periodic structure sample with three 0.8 mm bar patterns and it can be resolved well at 0.3 THz. The resolution is 0.32 times of the physical size of the focused beam. In addition, they have successfully measured the diameter of human hair with a relative error of less than 10% at 3 THz.
QI's work demonstrates a promising method that will be helpful for providing clearer imaging for scientific and biomedical applications.
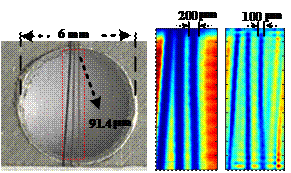
THz imaging of Human hair. From left: photo of hair sample, THz image before enhancement, THz image after enhancement.(Image by QI Feng)