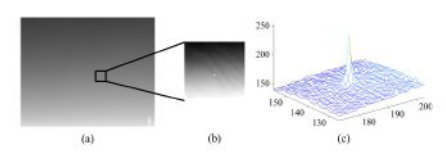
Dim targtet in real-scene IR image: (a) real-scene IR image, (b) enlarged view of dim target with contrast streching, and (c) 3-D display of dim target in (a). (Image from the origial paper)
Dim targets are extremely difficult to detect using methods based on single-frame detection. Radiation accumulation is one of the effective methods to improve signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). A detection approach based on radiation accumulation is proposed. First, a location space and a motion space are established. Radiation accumulation operation, controlled by vectors from the motion space, is applied to the original image space. Then, a new image space is acquired where some images have an improved SNR. Second, quasitargets in the new image space are obtained by constant false-alarm ratio judging, and location vectors and motion vectors of quasitargets are also acquired simultaneously. Third, the location vectors and motion vectors are mapped into the two spaces, respectively. Volume density function is defined in the motion space. Location extremum of the location space and volume density extremum of motion space will confirm the true target. Finally, actual location of the true target in the original image space is obtained by space inversion. The approach is also applicable to detect multiple dim targets. Experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed approach and demonstrate the approach is superior to compared approaches on detection probability and false alarm probability.
This work was published on Optical Engineering,2016,55(3):1-14. titled Rectilinear-motion space inversion-based detection approach for infrared dim air targets with variable velocitie.