Much to the surprise of many engineers, compares with conventional shot peening, high-pressure torsion, laser hardening, water-jet peening, and cold rolling in terms of mechanical performance improvement, depth of compression layer and high level of stability, laser shock peening is the most effective surface treatment method. So, laser shock peening has been applied to a variety of alloys used in aircraft engines, airframes, and other engineering applications.
For decades, two-phase γ-TiAl based alloys have received considerable attention for high temperature structural applications in aerospace and automotive industries. Plenty of studies have been conducted on the mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of these materials. However, in the literature to date, there are few reports the effect of laser shock peening on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAl alloy.
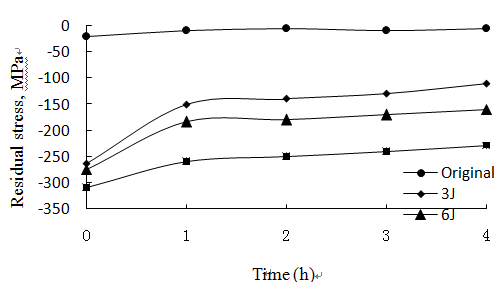
In order to study the effect of laser peening on microstructures and properties of TiAl alloy, TiAl alloy samples were treated by Nd: YAG laser system with the wavelength of 1064nm, pulse-width of 18ns, and pulse-energy of 0-10J. The experimental results show that surface micro-hardness increased by up to 30%, roughness increased to 0.37μm, compressive residual stress increased to 337MPa, local textures and typical lamellar microstructures were generated. Residual stress, micro-hardness, and (002) pole figures tests were conducted, compressive residual stress value drop from 337MPa to 260MPa, hardness value drop from 377HV0.2 to 343HV0.2, and the (002) poles shift back to the center slightly.
Effect of residual stress on treatment time(700℃) (Image prvided by SIA)
This study was co-supported by the National 863 Program (No. 2012AA041310). Papers related to this result were published on Chinese Journal of Aeronautics (Qiao Hongchao, Zhao jibin, Gao Yu. Experiment investigation of laser peening on TiAl alloy microstructure and properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(2): 609-616 DOI: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.01.006).
Contact:
QIAO Hongchao
Email: hcqiao@sia.cn
Shenyang Institute of Automation Chinese Academy of Science