Transmission as a main component of a modern automobile has a significant impact on vehicle performance, its technical parameters and working conditions is an important indicator to evaluate the automobile performance. For traditional transmission quality test, inspection work mainly rely on manual, this test method is called the original fault diagnosis, which depends on worker’s feeling, hearing, and experience. The method cannot adapt to continuous, stable, efficient requirements of modern production, and it is difficult to locate failure to specific parts, and cannot provide transmission repair guidance. Existing research shows that fault analysis and signal processing method will determine efficiency and accuracy of fault diagnosis for automobile transmission. Fault detection of newly assembled automobile transmission is a more challenging research work than fault detection of the transmission used for a long time.
To handle this issue, researchers from Shenyang Institute of Automation (SIA), Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a knowledge representation, feature selection and fault classification method based on GA-BP learning algorithm for newly assembled transmission. Based on the methods, an on-line fault diagnosis system is designed and developed for newly assembled transmission quality inspection.
The researchers firstly proposed a synchronous data acquisition algorithm of the vibration signal and the speed signal, which provides accurate data for latter order calculations. They use improved FFT algorithm for spectral transformation after a lot of tests. Measuring position of the vibration sensor is shown in Fig. 1. The sensor measuring position is selected by tests and calculations to ensure that the acquired signal contains the vibratory signals of each part in the transmission.

Fig.1. Transmission test-bench and vibration sensor measuring point (Image provided by SHANG Wenli et.al)
Then, an improved genetic search strategy is employed for fault feature selection. The algorithm can effectively solve high dimensional feature selection problem with lower computational complexity, thereby improve the operating efficiency and accuracy of the system.Tendency fitness function average value of standard GA and improved GA algorithm for feature selection are described in Fig. 2.
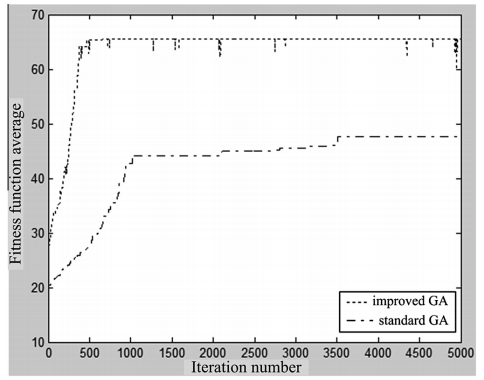
Fig.2. Change trend of fitness function average value of standard GA and improved GA algorithm (Image provided by SHANG Wenli et.al)
At last, fault classification method based on BP network is introduced. Low-dimension feature vectors obtained by improved GA are input into the neural network classifier for feature classification, which greatly improves efficiency of the classifier. Fig.3 shows the transmission fault diagnosis system, which supports two test modes: automatic control mode and manual control mode. The automatic control mode communicates automatically with test bench. The fault diagnosis system can detect four types of fault and find the specific fault part.
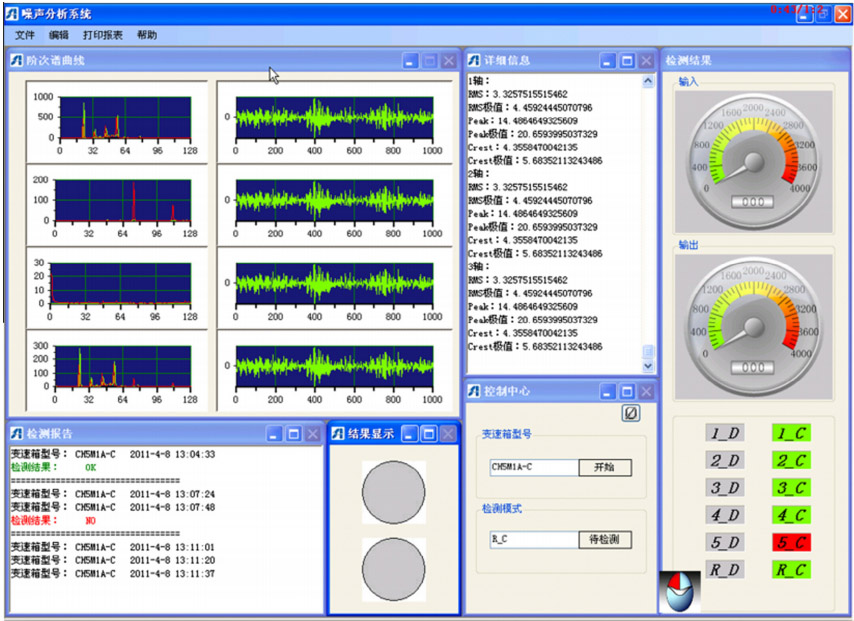
Fig.3 the transmission fault diagnosis system (Image provided by SHANG Wenli et.al)
Compared with traditional manual experiential inspection method, the system is efficient and stable. Specific part fault location provides valuable guidance for repair. The system has been applied in a transmission factory. Each gear detection cycle from acceleration to deceleration is 8s for newly assembled transmission, and overall fault detection algorithm proposed is fully capable of reaching industrial site real-time requirements.
This work was published on the journal of Expert systems with Applications, Volume 41, Issue 9, July 2014, 4060-4072. It was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 60904047, 61164012), by the Hi-tech Research and Development Program of China Funding (Grant No. 2007AA04Z1A4).
CONTACT:
Prof. SHANG Wenli
Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: shangwl@sia.cn