Inside the operation room of Chinese PLA General Hospital, a patient was taking a digestive tract inspection. It was performed by a robot.
It was the first clinical test of Flexible Endoscope Manipulation Robot (FEMR) assisted digestive tract intervention in the world, which was jointly carried out by researchers from Shenyang Institute of Automation Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIACAS) and Chinese PLA General Hospital (PLAGH) on December 20, 2017. Professor YANG Yunsheng, Chairman of digestive disease branch, Chinese Medical Association, manipulated the robot and realized the inspection along the upper digestive tract.
FEMR was developed by a research team led by LIU Hao, researcher from SIACAS, under the support of National Key Technology Research Development Program in 12th Five-Year.
According to LIU, FEMR has changed the traditional mode of endoscopic operation fundamentally. “It spares the doctors’ effort of standing beside patients while holding the endoscope; they can only operate the joysticks to complete the clinical operation.” LIU said.
FEMR was developed and passed the General Safety Test (GB 9706.1) and EMC Test (YY0505) A series of ergonomics such as double arm configuration, Intuitionistic mapping and integrated irrigation and suction system were used in robot design to achieve accurate and safety operation of soft endoscope that obviously superior to the traditional operation in the multi degree of freedom coordination operation and the quantitative display of operating parameters.
FEMR was a breakthrough in the field of surgical robot. At present, DaVinci surgical robot had great achievements and comprehensive monopoly in thoracic and abdominal minimally invasive surgery, but incapable for diagnosis and treatment in intracavities such as digestive, urinary and respiratory system. The development of FEMR has a great prospect of clinical application. (Shenyang Institute of Automation)
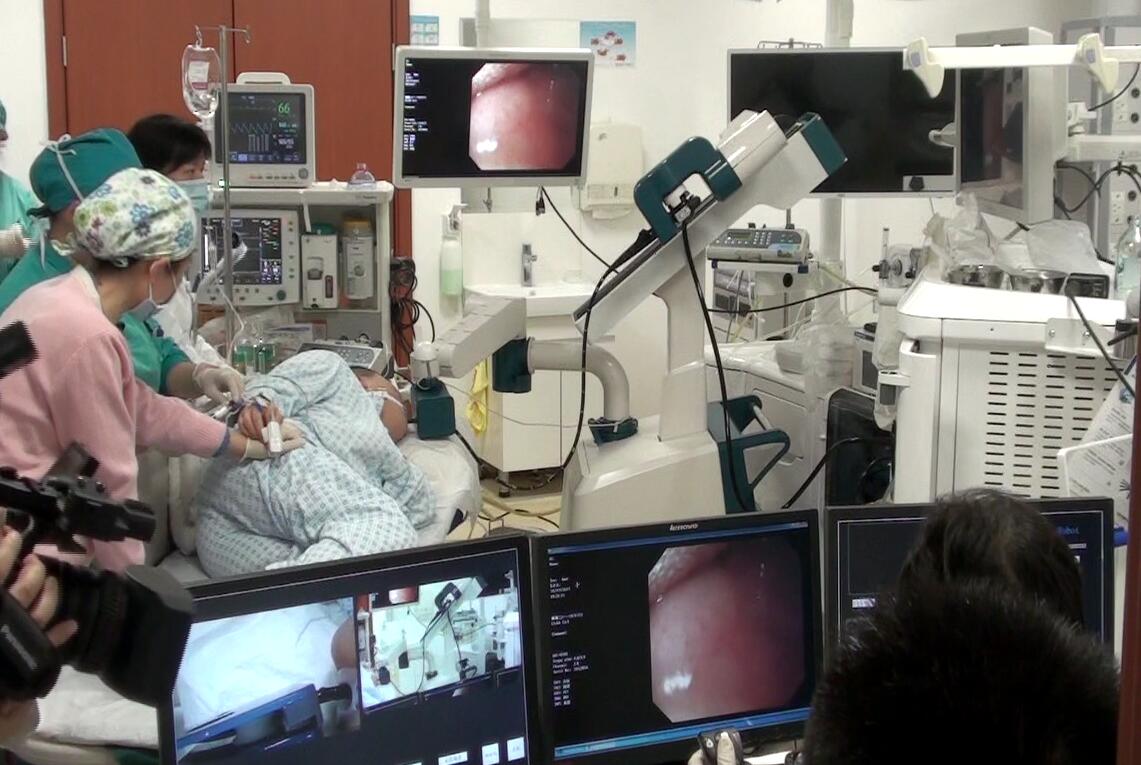
FEMR was performing operation. (Image by SIA)